gempy.create_geomodel¶
- gempy.create_geomodel(*, project_name: str = 'default_project', extent: list | ndarray | None = None, resolution: list | ndarray | None = None, refinement: int = 1, structural_frame: StructuralFrame | None = None, importer_helper: ImporterHelper | None = None, intpolation_options_tye: InterpolationOptionsType = InterpolationOptionsType.OCTREE) GeoModel[source]¶
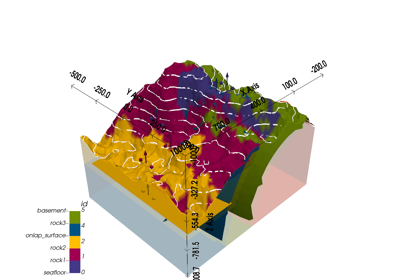
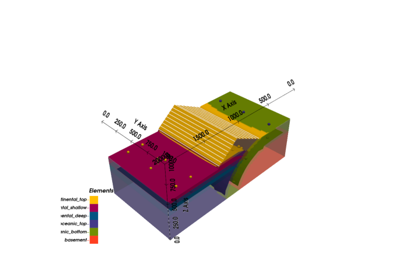
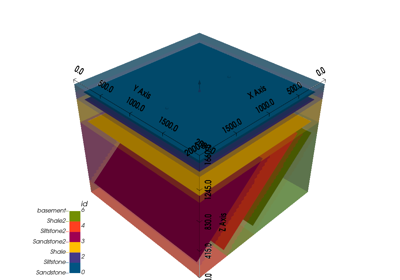
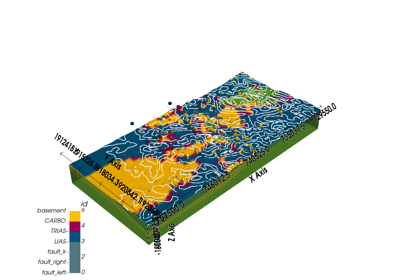
Creates a geological model based on input parameters, spatial configuration, and interpolation options.
This function initializes a geological model by defining the grid (dense grid or octree-based), selecting interpolation options based on the desired type, and configuring the structural frame using either a provided structural frame or an importer helper instance. The geological model is tailored for specific project-based requirements and can be either dense or with variable resolution depending on the refinement level.
- Parameters:
project_name (str) – Name of the geological model project. Defaults to ‘default_project’.
extent (list, ndarray) – Spatial extent of the geological model in the form of [min_x, max_x, min_y, max_y, min_z, max_z].
resolution (list, ndarray) – Resolution of the model grid in the form [x_res, y_res, z_res]. If not provided, the function will default to octree initialization.
refinement (int) – Refinement level for the octree grid. Ignored if resolution is provided. Defaults to 1.
structural_frame (StructuralFrame) – Pre-configured instance of StructuralFrame for the geological model. If not provided, an importer_helper must be supplied.
importer_helper (ImporterHelper) – Helper object for initializing a structural frame if none is explicitly provided.
intpolation_options_tye (InterpolationOptionsType) – Enum representing the desired type of interpolation options. Defaults to InterpolationOptionsType.OCTREE.
- Returns:
An initialized geological model with specified spatial configuration and interpolation properties.
- Return type:
- Raises:
ValueError – If neither structural_frame nor importer_helper is provided.
ValueError – If the interpolation options type is unrecognized.